Take Care To Protect Your Skin Especially in The Summer Months
Skin Cancer….What Types Are There?
Too much sun can cause skin cancer, so protect your skin especially in the summer. There are three types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Each type is unique, produces different symptoms, and has varying treatment methods.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Of all skin cancer, 75% is basal cell, making it the most common skin cancer. It is most commonly found on the face, neck and hands. It is highly treatable and rarely spreads to other parts of the body. Symptoms include a sore that oozes or bleeds, a redness area that is irritated, a yellow or white area that resembles a scar and a pink pearly bump. This type of cancer is most commonly the result of overexposure to the sun.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell is the second-most common type of skin cancer. It usually develops in places on the body that have been exposed to the sun, like ears, the face and the mouth, but can develop anywhere. Symptoms include a bump that turns into an open sore that doesn’t heal. If untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous and deadly type of skin cancer. It can develop on any part of the body however the arms, legs and trunk are the most common areas. When detected early, it is highly treatable. Symptoms include a mole, freckle or spot which changes in color, size and shape. It may have an irregular outline and possibly be more than one color. It is dangerous and potentially fatal because it can spread to other organs.
What Are The Treatments?
Skin cancer is fairly easily and quickly removed. Surgery is the most common treatment, but topical chemotherapy and radiation may sometimes used.
The most popular surgeries for skin cancer are excisional skin surgery where the surgeon removes the cancer with a scalpel, and Mohs surgery where the surgeon shaves away thin layers of skin until there are no more cancerous cells seen.
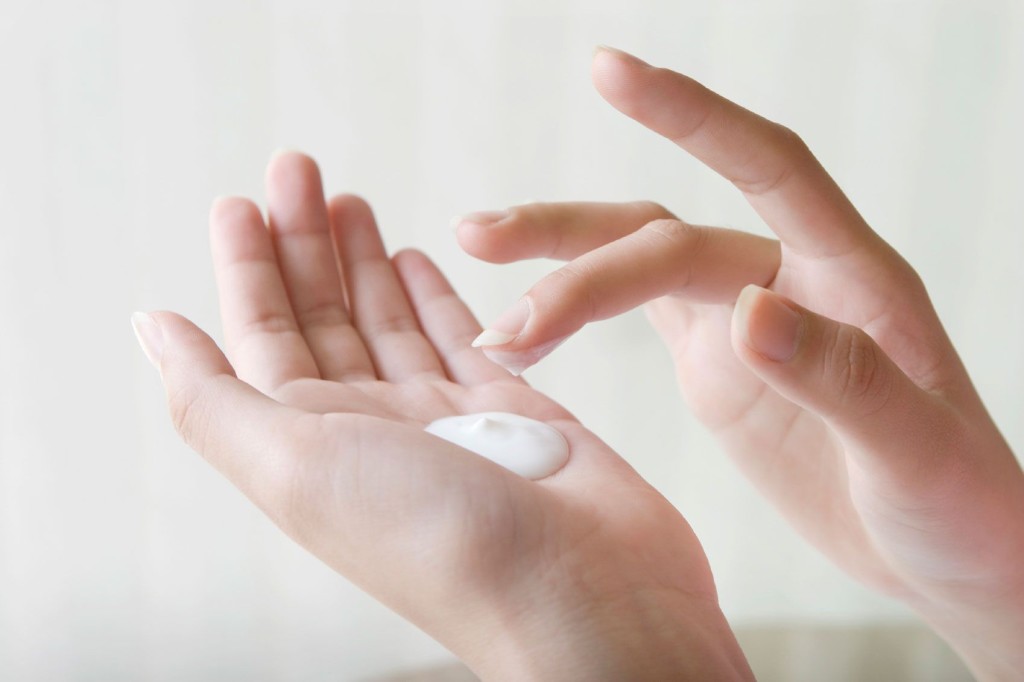
Topical chemotherapy is the use of lotions and creams. The anti-cancer drugs fluorouracil and imiquimod are effective in the treatment of both basal cell and squamous cell cancers. These topical creams are typically applied one or two times a day for several weeks.
Radiation therapy uses concentrated, high-energy rays to target and destroy cancerous cells. Radiation therapy is not a common treatment for skin cancer but is used if surgery is not an option.
Can I Reduce My Risk of Skin Cancer?
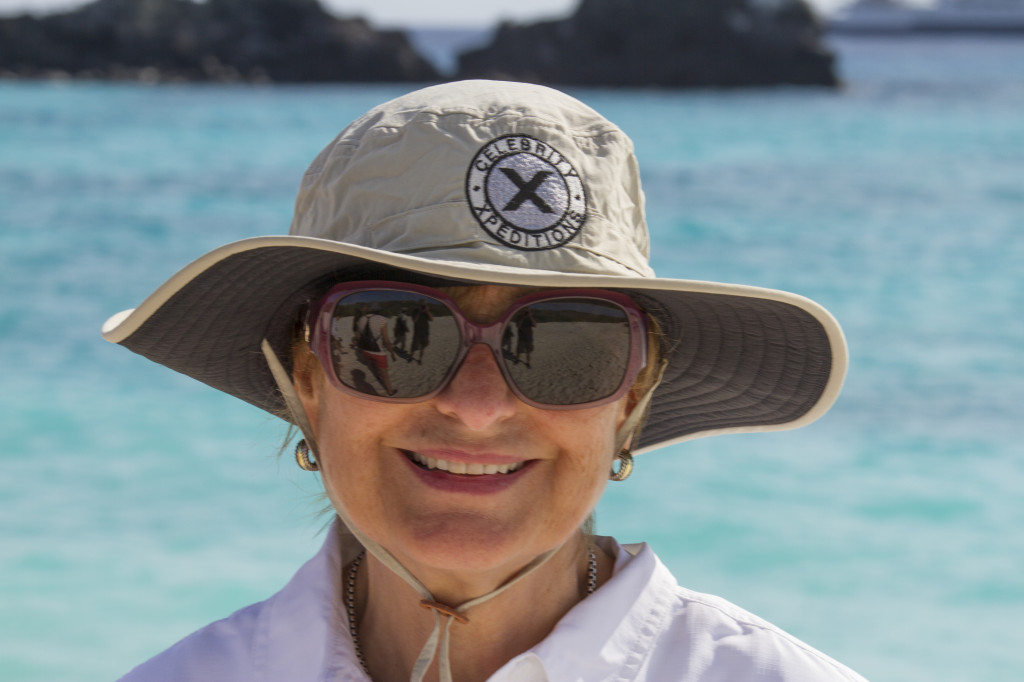
Yes! Protect yourself from the ultraviolet rays of the sun especially during the summer. The sun is strongest between 10 am and 4 pm. Try to stay in the shade, wear loose-fitting clothing that covers your arms and legs. Wear a hat with a wide brim to shade your face, head, ears and neck. Wear sunglasses that block both UVA an UVB rays. Use sunscreen with a “sun protective factor” (SPF) 15 or higher. Avoid indoor tanning.
How Does Sunscreen Work?
Sunscreen works by absorbing, reflecting or scattering sunlight. Chemicals in the product interact with the skin to protect it. Also watch the expiration date on sunscreen before using.
If you are fair-skinned and burn easily, have a large number of moles, or if you have a family history of skin cancer, be sure to take precautions when in the sun. If you have a question about skin care, call AW Health Care at (314) 726-5600 for help.






Comments are closed.